Race Distances:
Triathlon Jargon
For those new to triathlon, below is a list of some of the key terms to help ease your transition into the sport.
Aerobars
Also known as tri-bars, the aerodynamic handlebars used in racing that puts the rider in a low, aero-dynamic “praying mantis” position.
Aerobic
The use of oxygen in the body’s energy-generating process during moderate intensity exercise. Aerobic exercise involves or improves oxygen consumption by the body.
Age grouper
All triathletes who are not professional are termed “age groupers”.
Anaerobic
When your body produces energy without utilising oxygen, stimulated by exercise that’s at high intensity.
Base training
Low-intensity training that stimulates your aerobic system and helps develop endurance.
Bilateral breathing
Breathing on alternate left/right sides when swimming, typically every third or fifth stroke.
Bonk or Bonking
A rapid drop in energy caused by the depletion of glycogen in the muscles and liver. Also called ‘the wall’ by runners, it can be accompanied by nausea, dizziness and even hallucinations and is the result of not refuelling sufficiently.
Brick session
A brick session combines multiple disciplines, for example a swim followed by a bike or a bike followed by a run.
Cadence
The rate at which you’re pedalling or running, expressed in revolutions per minute (rpm) or steps per minute. The cadence refers to one leg only; for example, 90rpm would mean either the right leg or left leg performed 90 complete pedal strokes in one minute.
Catch
The point in the swim stroke when swimmers apply pressure to the water to help propel them forward.
Core stability
The ability to control the position and movement of the central portion of the body, in particular control of spinal stability. Training targets the deep spinal stabilising muscles rather than the superficial abdominal muscles.
Drafting
Hitching a ride in someone else’s slipstream. The draft zone varies in size depending on the race. Drafting is not permitted in most age-group races but is allowed in elite ITU racing. Penalties vary per race, but typically can involve a 15 second time penalty.
Drills
A number of different exercises to improve your technique and/or speed in any of the three disciplines.
Functional threshold pace (FTP)
The maximal effort you can sustain over roughly a 45-60 minute duration. A 10km race or 25km bike time trial would be a good rough indication of you FTP by working out your pace per km/mile.
HIIT
High intensity interval training.
HRmax
Your maximum heart rate, measured in beats per minute.
Interval training
Intensive training using repeated on/off effort. Usually employed to develop speed and work the aerobic system.
“Ironman” (for official Ironman branded events), iron distance or long distance
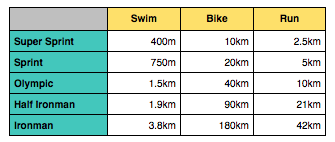
Ironman is the original long-distance triathlon raced in Hawaii.
3.8km swim, 180km bike and a 42.2km run. You must complete the race in less than 17 hours (with exceptions such as France and Germany, with 16- and 15-hour limits respectively).
“Ironman 70.3” (for official Ironman events), Half-Ironman or middle distance
70.3 refers to the total distance of the race in miles. 1.9km swim, 90km bike and a 21km run.
Lactic acid
Produced in the muscles during high-intensity workouts, it can inhibit oxygen movement and slow you down.
Mount zone
The area just beyond transition for mounting your bike before starting the bike leg. On the return leg, this is where you must dismount before entering transition.
Negative splits
A training method where successive sets are completed faster than the previous one. In a race context, it is where you pace yourself to race the second half faster than the first half.
Olympic or standard distance
Refers to a race that follows the format of the Olympic-recognised triathlon. 1.5km swim, 40km bike and a 10km run.
Overtraining
Common symptoms of training too much with insufficient recovery include insomnia, headaches, moodiness, loss of enthusiasm for the sport and increased illness due to a suppressed immune system.
Sprint distance
Half the distance of a standard distance triathlon, these may involve an indoor or outdoor swim. 750m swim, 20km bike and a 5km run.
Super sprint distance
Ideal for those new to triathlon, these events often have an indoor or pool swim. 400m swim, 10km bike and a 2.5km run.
T1
Transition one: swim to bike.
T2
Transition two: bike to run.
Taper
Reducing your activity in the days/weeks leading up to a race. For shorter events the taper period may only be a few days. For middle and long distance events this could start over a period of weeks prior to your event.
Transition
The area where you go to change kit between the disciplines. Sometimes called the fourth discipline.
Turbo trainer
A frame that attaches to your bike and provides resistance to the back wheel as you pedal. This turns the bike into a static trainer and is useful for bad weather and/winter training.
Useful websites
The national governing body for triathlon, duathlon and aquathon in Great Britain
http://www.triathlonengland.org/
Triathlon England is one of three Home Nation bodies for Triathlon in Great Britain.
If you reside in England or are eligible to represent England you should join Triathlon England. Members will be affiliated to a region and can vote for their Regional Committee.
220 Triathlon is the UK’s longest-running and most popular magazine for all things triathlon- related, with each issue providing the latest news, race coverage, training/nutrition advice and gear reviews.
VO2max
A measure of the body’s maximal ability to use oxygen to produce energy. Those who are fitter will have a higher VO2max.
Watt
The unit of measurement in which power is expressed.
Waves
Where competitors are split into start waves or groups, often by age group or predicted finish time.


